Difference between revisions of "Course:OL Delivery:OTL101:Planning"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
ColinMadland (talk | contribs) |
ColinMadland (talk | contribs) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [ | + | == Cognitive Presence - Assessment and Feedback to Maximize Student Learning== |
| + | ====Akyol, Z., & Garrison, D. R. (2011). Understanding cognitive presence in an online and blended community of inquiry: Assessing outcomes and processes for deep approaches to learning. British Journal of Educational Technology, 42(2), 233–250. [http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/enhanced/doi/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2009.01029.x/ doi:10.1111/j.1467-8535.2009.01029.x]==== | ||
| − | + | *''Notwithstanding the strengths of online communities to support higher levels of learning through sustained discourse and reflection, assessing the quality of learning outcomes associated with deep approaches to learning has been an ongoing challenge. The point is that we need to focus on assessing actual learning outcomes in order to associate depth of learning with interactive and collaborative approaches to online and blended learning. If we are to understand how to support cognitive presence in online and blended learning communities, then greater focus needs to be placed on linking processes and outcomes.'' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *''Practical Inquiry Model (process of critical thinking) http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/enhanced/doi/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2009.01029.x/#figure-viewer-f1'' | |
| − | + | **Triggering event: This phase initiates the inquiry process through a well-thought out activity to ensure full engagement and buy-in from the students. This has several positive outcomes in terms of involving students, assessing the state of knowledge and generating unintended but constructive ideas. | |
| + | **Exploration: This phase focuses first on understanding the nature of the problem and then searching for relevant information and possible explanation. | ||
| + | **Integration: This phase moves into a more focused and structured phase of constructing meaning. Decisions are made about integration of ideas and how order can be created parsimoniously. | ||
| + | **Resolution: This phase is the resolution of the dilemma or problem, whether that is reducing complexity by constructing a meaningful framework or discovering a contextually specific solution. This confirmation or testing phase may be accomplished by direct or vicarious action. | ||
| + | *''As Marton (1988) states, ‘what is learned (the outcome or the result) and how it is learned (the act or the process) are two inseparable aspects of learning’ (p. 53).'' | ||
| + | *'' Garrison and Cleveland-Innes (2005) suggested that high levels of critical thinking and learning is dependent on structured and coherent interaction or discourse. The Study Process Questionnaire (Biggs, 1987), used to measure approaches to learning, was administered to online course participants in four graduate courses that were selected based on differences in required interaction and instructor presence. Findings suggested that interaction by itself does not promote deep approaches to learning. It was concluded ‘that the quality of interaction (ie, critical discourse) must be a specific design goal and interaction facilitated and directed in a sustained manner if deep approaches to learning are to be achieved’ (p. 142). Deep learning would appear to be associated with the quality of the engagement and suggests focused and coherent collaborative communities of inquiry.'' | ||
| − | == | + | ====Arbaugh, J. B., Cleveland-Innes, M., Diaz, S. R., Garrison, D. R., Ice, P., Richardson, J. C., & Swan, K. P. (2008). Developing a community of inquiry instrument: Testing a measure of the Community of Inquiry framework using a multi-institutional sample. Special Section of the AERA Education and World Wide Web Special Interest Group (EdWeb/SIG), 11(3–4), 133–136. [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1096751608000250 doi:10.1016/j.iheduc.2008.06.003]==== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ====Garrison, D. R., & Cleveland-Innes, M. (2005). [http://dx.doi.org/10.1207/s15389286ajde1903_2 Facilitating cognitive presence in online learning: Interaction is not enough]. American Journal of Distance Education, 19, 133–148.==== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | * | |
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | ====Shea, P., & Bidjerano, T. (2009). Cognitive presence and online learner engagement: a cluster analysis of the community of inquiry framework. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 21(3), 199–217. [http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12528-009-9024-5/fulltext.html doi:10.1007/s12528-009-9024-5]==== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | * | |
| − | + | ||
| − | ==== | + | ====http://cguevara.commons.gc.cuny.edu/files/2009/09/Learning-Effectiveness-paper-Garrison.pdf==== |
| − | * | + | * |
| − | |||
| − | ==== | ||
| − | |||
| + | ====http://sloanconsortium.org/jaln/v11n1/online-community-inquiry-review-social-cognitive-and-teaching-presence-issues==== | ||
| − | + | * | |
| − | ==== | + | ====Kanuka, H., & Garrison, D. R. (2004). Cognitive presence in online learning. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 15(2), 21–39. [http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02940928# doi:10.1007/BF02940928]==== |
| − | |||
| − | + | * | |
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Overview== |
| − | + | explores factors that impact the learner’s cognitive presence and sustain deep learning. You will have opportunities to develop feedback strategies in relation to assessment and those which will encourage deeper student learning. | |
| − | ==== | + | ==Outcomes== |
| − | + | # analyze the characteristics of ‘cognitive presence’ in an effective online learning environment | |
| − | + | # explain the importance of deep approaches to learning in relation to assessment, feedback and student attainment of learning outcomes. | |
| + | # evaluate the quality of the feedback that they provide for students in light of relevant evidence-based research (SOLO Taxomony and [http://%20http://rer.sagepub.com/content/77/1/81.abstract Hattie & Timperley]. | ||
| + | # analyze learning activities and their effectiveness to promote deep approaches to learning | ||
| + | # provide high quality feedback using appropriate tools to promote deep approaches to learning. | ||
| + | # create an environment that supports and enhances deeper approaches to learning in your courses | ||
| + | # monitor your progress towards achieving your goals resulting in an improved and enhanced cognitive presence in your courses. | ||
| + | ==Links== | ||
| + | *[[Teaching_and_Learning_Resources_Portal/Distance_Technologies/Feedback|Feedback resources from OLFM Workshop]] | ||
| + | *[http://cmadland.wikispaces.com/Quality+Feedback Outside the Box Feedback] | ||
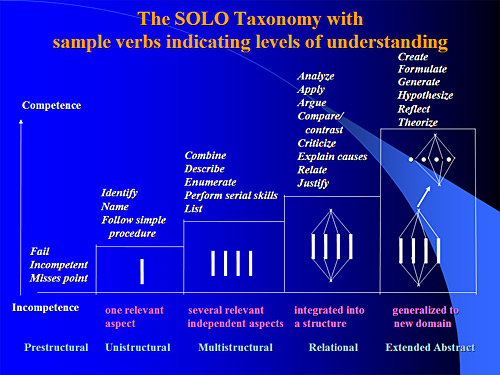
| + | *SOLO Taxonomy | ||
| + | ::http://www.johnbiggs.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/solo_taxonomy.jpg | ||
| − | ===Week | + | ==Course Overview== |
| + | ===Week 1 - Welcome and Intro=== | ||
====Outcome==== | ====Outcome==== | ||
| − | |||
====Activities==== | ====Activities==== | ||
| − | + | *Draw yourself as...? | |
| − | * | + | * Wordle? |
| − | |||
====Resources==== | ====Resources==== | ||
====Assessments==== | ====Assessments==== | ||
| − | ===Week | + | ===Week 2-3 - Deep Approaches to Learning=== |
====Outcome==== | ====Outcome==== | ||
====Activities==== | ====Activities==== | ||
| + | #Analyze and explain how various qualities of feedback might influence student learning | ||
| + | |||
====Resources==== | ====Resources==== | ||
====Assessments==== | ====Assessments==== | ||
| − | + | ===Week 4-5 - SOLO Taxonomy=== | |
| − | ===Week | ||
====Outcome==== | ====Outcome==== | ||
====Activities==== | ====Activities==== | ||
| + | #analyze feedback on sample student work in light of SOLO and Hattie & Timperley's model. | ||
| + | #analyze one learning activity from one of your courses and explain how it aligns to the intended learning outcomes of the course, how the activity is strucutred to support student learning and what level of the SOLO taxonomy is required in student responses | ||
| + | #*suggest changes to enhance the quality of the activity | ||
| + | #provide examples of high quality feedback using appropriate tools or media | ||
| + | |||
====Resources==== | ====Resources==== | ||
====Assessments==== | ====Assessments==== | ||
| − | ===Week | + | ===Week 6 - Goals for Enhancing Cognitive Presence=== |
====Outcome==== | ====Outcome==== | ||
====Activities==== | ====Activities==== | ||
| − | *Review and summarize 2-3 current articles on enhancing | + | *Review and summarize 2-3 current articles on enhancing cognitive presence and identify 2-3 goals relevant to your work |
| − | *Present strategies for achieving your goals | + | *Present strategies for achieving your goals...develop a plan |
====Resources==== | ====Resources==== | ||
====Assessments==== | ====Assessments==== | ||
| + | ====Reflective Questions==== | ||
| + | * What do I know about now that I didn’t know when I started? | ||
| + | * Why did this particular (event, barrier, success, accident) happen? How can it be explained? | ||
| + | * What can I do differently next time? How could I have made this go faster, better, more smoothly? | ||
| + | * What political issues emerged? | ||
| + | * A problem I ran into was ___________________ | ||
| + | * I fixed it, overcame it, or circumvented it by ______________________ | ||
| + | * How did the outcome measure up to my expectations? | ||
| + | * How well did the actual reflect my estimates on time, challenges, difficulty, or people? | ||
| + | * I could not fix, overcome, or circumvent it because ___________________ | ||
| + | * Did this highlight any deficiencies in my preparation, training, or skill level? What do I need to do to correct that? | ||
| + | * What assumptions did I make? How valid were these? How did they affect what I did? | ||
| + | * What do I know about __________ now that I didn’t know when I started? | ||
| + | * Why did ___________ happen? How I explain it? | ||
| + | * What did I learn from this? | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://blog.talentlms.com/reflective-practice-companys-lms/ | ||
Latest revision as of 10:02, 22 July 2014
Cognitive Presence - Assessment and Feedback to Maximize Student Learning
Akyol, Z., & Garrison, D. R. (2011). Understanding cognitive presence in an online and blended community of inquiry: Assessing outcomes and processes for deep approaches to learning. British Journal of Educational Technology, 42(2), 233–250. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8535.2009.01029.x
- Notwithstanding the strengths of online communities to support higher levels of learning through sustained discourse and reflection, assessing the quality of learning outcomes associated with deep approaches to learning has been an ongoing challenge. The point is that we need to focus on assessing actual learning outcomes in order to associate depth of learning with interactive and collaborative approaches to online and blended learning. If we are to understand how to support cognitive presence in online and blended learning communities, then greater focus needs to be placed on linking processes and outcomes.
- Practical Inquiry Model (process of critical thinking) http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/enhanced/doi/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2009.01029.x/#figure-viewer-f1
- Triggering event: This phase initiates the inquiry process through a well-thought out activity to ensure full engagement and buy-in from the students. This has several positive outcomes in terms of involving students, assessing the state of knowledge and generating unintended but constructive ideas.
- Exploration: This phase focuses first on understanding the nature of the problem and then searching for relevant information and possible explanation.
- Integration: This phase moves into a more focused and structured phase of constructing meaning. Decisions are made about integration of ideas and how order can be created parsimoniously.
- Resolution: This phase is the resolution of the dilemma or problem, whether that is reducing complexity by constructing a meaningful framework or discovering a contextually specific solution. This confirmation or testing phase may be accomplished by direct or vicarious action.
- As Marton (1988) states, ‘what is learned (the outcome or the result) and how it is learned (the act or the process) are two inseparable aspects of learning’ (p. 53).
- Garrison and Cleveland-Innes (2005) suggested that high levels of critical thinking and learning is dependent on structured and coherent interaction or discourse. The Study Process Questionnaire (Biggs, 1987), used to measure approaches to learning, was administered to online course participants in four graduate courses that were selected based on differences in required interaction and instructor presence. Findings suggested that interaction by itself does not promote deep approaches to learning. It was concluded ‘that the quality of interaction (ie, critical discourse) must be a specific design goal and interaction facilitated and directed in a sustained manner if deep approaches to learning are to be achieved’ (p. 142). Deep learning would appear to be associated with the quality of the engagement and suggests focused and coherent collaborative communities of inquiry.
Arbaugh, J. B., Cleveland-Innes, M., Diaz, S. R., Garrison, D. R., Ice, P., Richardson, J. C., & Swan, K. P. (2008). Developing a community of inquiry instrument: Testing a measure of the Community of Inquiry framework using a multi-institutional sample. Special Section of the AERA Education and World Wide Web Special Interest Group (EdWeb/SIG), 11(3–4), 133–136. doi:10.1016/j.iheduc.2008.06.003
Garrison, D. R., & Cleveland-Innes, M. (2005). Facilitating cognitive presence in online learning: Interaction is not enough. American Journal of Distance Education, 19, 133–148.
Shea, P., & Bidjerano, T. (2009). Cognitive presence and online learner engagement: a cluster analysis of the community of inquiry framework. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 21(3), 199–217. doi:10.1007/s12528-009-9024-5
http://cguevara.commons.gc.cuny.edu/files/2009/09/Learning-Effectiveness-paper-Garrison.pdf
http://sloanconsortium.org/jaln/v11n1/online-community-inquiry-review-social-cognitive-and-teaching-presence-issues
Kanuka, H., & Garrison, D. R. (2004). Cognitive presence in online learning. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 15(2), 21–39. doi:10.1007/BF02940928
Overview
explores factors that impact the learner’s cognitive presence and sustain deep learning. You will have opportunities to develop feedback strategies in relation to assessment and those which will encourage deeper student learning.
Outcomes
- analyze the characteristics of ‘cognitive presence’ in an effective online learning environment
- explain the importance of deep approaches to learning in relation to assessment, feedback and student attainment of learning outcomes.
- evaluate the quality of the feedback that they provide for students in light of relevant evidence-based research (SOLO Taxomony and Hattie & Timperley.
- analyze learning activities and their effectiveness to promote deep approaches to learning
- provide high quality feedback using appropriate tools to promote deep approaches to learning.
- create an environment that supports and enhances deeper approaches to learning in your courses
- monitor your progress towards achieving your goals resulting in an improved and enhanced cognitive presence in your courses.
Links
Course Overview
Week 1 - Welcome and Intro
Outcome
Activities
- Draw yourself as...?
- Wordle?
Resources
Assessments
Week 2-3 - Deep Approaches to Learning
Outcome
Activities
- Analyze and explain how various qualities of feedback might influence student learning
Resources
Assessments
Week 4-5 - SOLO Taxonomy
Outcome
Activities
- analyze feedback on sample student work in light of SOLO and Hattie & Timperley's model.
- analyze one learning activity from one of your courses and explain how it aligns to the intended learning outcomes of the course, how the activity is strucutred to support student learning and what level of the SOLO taxonomy is required in student responses
- suggest changes to enhance the quality of the activity
- provide examples of high quality feedback using appropriate tools or media
Resources
Assessments
Week 6 - Goals for Enhancing Cognitive Presence
Outcome
Activities
- Review and summarize 2-3 current articles on enhancing cognitive presence and identify 2-3 goals relevant to your work
- Present strategies for achieving your goals...develop a plan
Resources
Assessments
Reflective Questions
* What do I know about now that I didn’t know when I started? * Why did this particular (event, barrier, success, accident) happen? How can it be explained? * What can I do differently next time? How could I have made this go faster, better, more smoothly? * What political issues emerged? * A problem I ran into was ___________________ * I fixed it, overcame it, or circumvented it by ______________________ * How did the outcome measure up to my expectations? * How well did the actual reflect my estimates on time, challenges, difficulty, or people? * I could not fix, overcome, or circumvent it because ___________________ * Did this highlight any deficiencies in my preparation, training, or skill level? What do I need to do to correct that? * What assumptions did I make? How valid were these? How did they affect what I did? * What do I know about __________ now that I didn’t know when I started? * Why did ___________ happen? How I explain it? * What did I learn from this?