Teaching and Learning Resources Portal/Distance Technologies/Student Approach to Learning
Editing the Wiki
Wiki use in Education: Sample
Encouraging Students to take Deeper Approaches to their learning.
Examples of deeper learning
Deeper learning defined as
Taking knowledge and can apply to novel situations. Start to question ideas. Critical thinking versus surface learning where you just have few ideas and be wrong. Misconceptions lead to a weak network of concepts. Motivated by interest. Need a hook to have it stay. Brain hurts - cognitive dissonance - confusion with material means on the path to deeper learning. Watch what you are testing.
- Why is a deep approach important? Transferable
, permanent
- What strategies do you use to promote deep approaches?
If you want students to think at higher levels you need to give them activities to apply and use materials.
Important to give example questions and allow practice.
Why is important. Not just facts.
Resources
- TRU Strategic Priorities
- Biggs, J., & Tang, C. (2007). Teaching for quality learning at university: What the student does (3rd ed.). New York: Society for Research into Higher Education & Open University Press. Retrieved from http://site.ebrary.com.ezproxy.tru.ca/lib/trulibrary/docDetail.action
- Biggs, J., Kember, D., & Leung, D. Y. P. (2001). The revised two-factor Study Process Questionnaire: R-SPQ-2F. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 71, 133–149. doi:10.1348/000709901158433
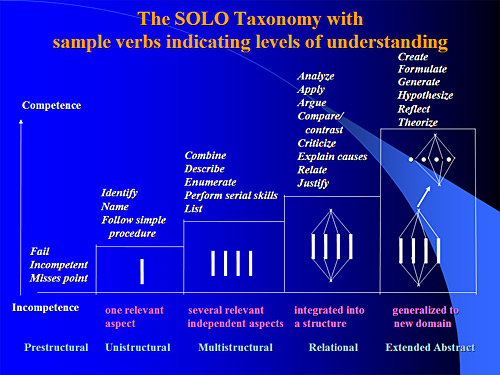
- Biggs, J., & Collis, K. (1982). Evaluating the quality of learning: The SOLO taxonomy. New York: Academic Press.
- Madland, C. (2014) Structured Student Interactions in Online Distance Learning: Exploring the study buddy activity. Athabasca University
- Edwards, J (2010) Inviting students to learn: 100 tips for talking effectively with your students.ASCD. Alexandria, Virginia.
- Kanuka, H. (2005). An exploration into facilitating higher levels of learning in a text-based Internet learning environment using diverse instructional strategies. Journal of Computer Mediated Communication, 10(3). [online]. Available: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1083-6101.2005.tb00256.x/full.
- Teaching Teaching and Understanding Understanding on YouTube
Carson Keever
Outcomes Based Deeper learning is identifying WHY something is happening seeing a pattern and understanding why the pattern is happening - students often assume the most complicated possible explanation - students are more concerned with being correct then understanding why things are happening - students have to be able to trust you - graduate school is a good example of needing to embark on deeper learning
cognitive dissidence (dissonance?): Sign that you are on the path to deeper understanding is confusion about a topic. When students are on the path to deeper learning you are often overloaded with information and not sure how to organize that information.
cognitive dissidence is difficult to assess
Operational Explanations Deeper approach: students high level cognitive skills for tasks that require them Surface approach: students use low level cognitive skills for tasks that require high level cognitive skills (John Biggs and Catherine Tang Teaching for Quality Learning at University)
Need to make learning activities reflect deeper understanding and not shallow learning outcomes Students wonder why they need to learn.
Integrating Deeper Learning into the Learning Process
Refer to Biggs et al. 2001
Presage, operational definition is what occurs prior to learning experience the student has had
Presage example, activate student prior learning or experience and goals in the beginning of the course Process example, keep students motivated toward their goal or their prior experience Product example, tie end results of student learning in with original goals
Time lag is a huge challenge in student presage in open learning
Students taking a course to apply directly to their working career, often have a better understanding of WHY they want to learn something. They have a better understanding of WHY because they have had more prior learning or experience in the field of study and they understanding how the course outcomes can benefit and improve their professional output.
Evaluation
How we can use evaluation to inform deeper learning The concept of Constructive Alignment Refer to Biggs Solo Taxonomy
Group 2 Notes
Group 3 Notes
Track 3 Effective Media http://truvideocamp.net tips and tricks http://barabus.tru.ca/cmdg use in-house marketing and You Tube to promote course.
Kong n Earle
SUrface vs deep learning
Deep -= understanding the why that happens; looking at the data to see other explanations Surface = the single event, following the pattern,
Geology Analogy: surface= the eruption of a volcano whereras deep = WHY it erupted the way it did and HOW can we predict a subsequent eruption
Real life example: medical lab tests = electrolyte levels surface: results suggest diabetes because lots of lab tests have diabetes
deep: true, there may be diabetes but the results also suggest that the electrolyte imbalance mean a heart attack is imminent.
Colin's example of a number pattern of 2, 4, 6.... - our first guess at what "the rule" is: a) What's your definition of rule b) adding by 2s c) fancy multiplication by factorials
HOwever, Colin's answer was that it was just ascending numbers. However, we all felt that it was a complicated answer because we (the students) made assumptions!!
Take home message: 1) get the students to ask the question: "what is the (definition) of the rule"? 2) students need to collect more data (ie see more numbers following Colin's pattern) in order to guess the answer (ie more deep learning)
QUotation for Biggs & Tang "Teaching for quality learnig at university" Deep learning = high level of cognitive skills for tasks which required fo them surface approach = use low level of cognitive skillsl for tasks which require high cognitive skills
There is a mismatch - and that's where the teaching problem is.
learning process figure
test
SOLO Taxonomy